XPRT Fitness Tricep Press Down Cable Attachment, V Handle with Rotation, Rotating Bar, Tricep Rope, V-Shaped Bar, Weight Machine Accessories Set of 4
XPRT Fitness Tricep Press Down Cable Attachment, V Handle with Rotation, Rotating Bar, Tricep Rope, V-Shaped Bar, Weight Machine Accessories Set of 4 provide constant tension on muscles when you do weight lifting. Engaged in a full range of motion.
-
$249.99
$499.98 -
Walking Desk Treadmill | LifeSpan TR1200-DT3
Rated 5.00 out of 504Walking Desk Treadmill | LifeSpan TR1200-DT3
Rated 5.00 out of 504 -
-
$45.99
$76.65
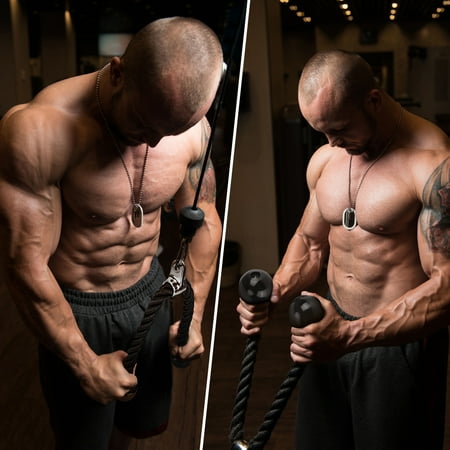
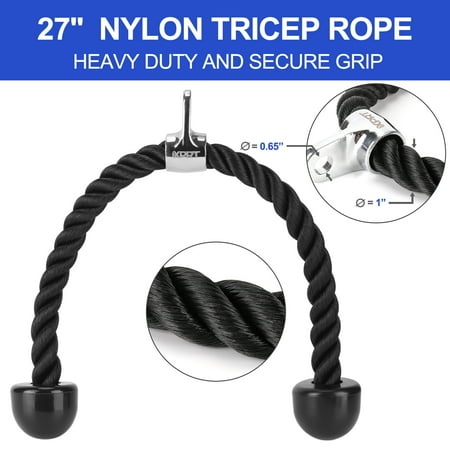
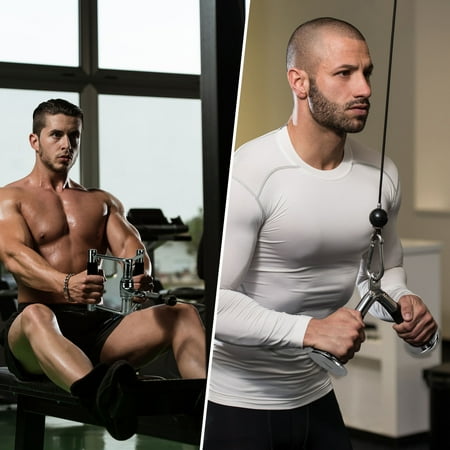

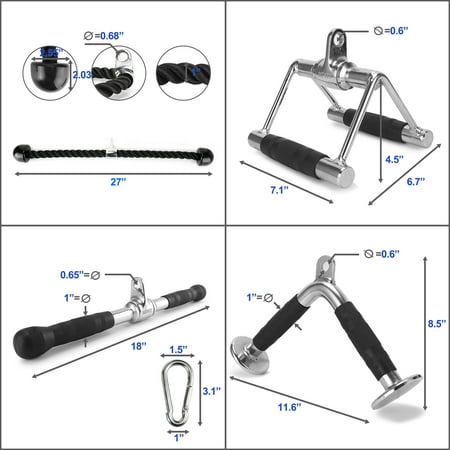
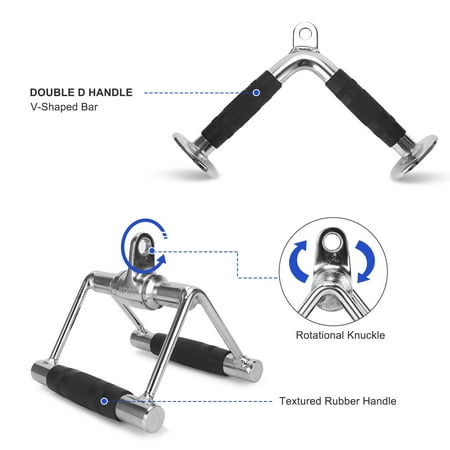




Set of 4 includes 4 high-quality essential gym cable attachments and one carabiner clipTricep Rope- Versatile attachment for various training. Heavy-duty Nylon braided rope with sturdy solid endcaps prevent hands from sliding off the rope, 360-degree chrome swivel hanger. Support up to 800 lbsRotating Steel Straight Bar – Chrome solid steel bar with textured anti-slip rubber coating handles, 360-degree swivel hanger. Support up to 800 lbsV Handle with Rotation also called Double D Handle – Chrome solid steel Handle with 360-degree swivel hanger, textured rubber coating on both handles provide secure grip and protection during trainingV-Shaped Bar – Anti-slipping ergonomic rubber coating on both ends of the solid V-shaped steel, 0.6-inch hole flat knob fits for all cable machines. Support up to 800 lbs1-year warranty. We stand by our products, if you are not 100% satisfied, please contact us and we will make it right





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.